-
Table of Contents
Clenbuterol in Nutritional Supplements for Athletes: Myth or Reality?
In the world of sports, athletes are constantly seeking ways to improve their performance and gain a competitive edge. This has led to the rise of nutritional supplements, which promise to enhance strength, endurance, and overall athletic performance. One such supplement that has gained popularity in recent years is clenbuterol. However, there is much debate surrounding its use in sports and whether it truly delivers the promised benefits. In this article, we will delve into the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of clenbuterol and examine the evidence behind its use in nutritional supplements for athletes.
The Basics of Clenbuterol
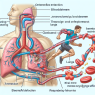
Clenbuterol, also known as “clen,” is a beta-2 adrenergic agonist that was originally developed to treat respiratory conditions such as asthma. However, it has gained attention in the sports world due to its ability to increase muscle mass and decrease body fat. It is often marketed as a “fat burner” and is commonly used by bodybuilders and athletes looking to improve their physique.
When taken orally, clenbuterol is rapidly absorbed and reaches peak plasma levels within 2-3 hours. It has a half-life of approximately 36 hours, meaning it can stay in the body for an extended period of time. This is important to note as it can potentially lead to accumulation and adverse effects if not used properly.
The Myth: Clenbuterol as a Performance Enhancer
Many athletes and bodybuilders believe that clenbuterol can enhance their performance by increasing muscle mass and decreasing body fat. However, there is limited scientific evidence to support these claims. In fact, a study by Knych et al. (2014) found that clenbuterol had no significant effect on muscle mass or strength in horses.
Furthermore, clenbuterol is not approved for use in humans by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is classified as a banned substance by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). This is due to its potential for abuse and adverse effects, which we will discuss in the next section.
The Reality: Adverse Effects of Clenbuterol
While clenbuterol may have some potential benefits, it also comes with a host of adverse effects. These include increased heart rate, tremors, anxiety, and insomnia. In severe cases, it can even lead to cardiac arrhythmias and heart failure. These effects are due to its ability to stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, which controls the “fight or flight” response in the body.
Moreover, clenbuterol has been found to have a negative impact on the cardiovascular system. A study by Kier et al. (2018) found that chronic use of clenbuterol in rats led to structural changes in the heart, including enlargement of the left ventricle and thickening of the heart muscle. This can increase the risk of cardiovascular events, especially in athletes who engage in intense physical activity.
The Controversy: Clenbuterol in Meat
One of the reasons for the confusion surrounding clenbuterol is its presence in meat. In some countries, clenbuterol is used as a growth promoter in livestock, which can lead to its presence in meat products. This has resulted in athletes testing positive for clenbuterol, claiming that they unknowingly consumed it through contaminated meat.
However, a study by Van Eenoo et al. (2010) found that the amount of clenbuterol present in meat is not enough to cause a positive drug test. This is due to the low bioavailability of clenbuterol when ingested orally. Therefore, it is unlikely that contaminated meat is the cause of positive drug tests in athletes.
The Bottom Line: Expert Opinion
Based on the available evidence, it is clear that clenbuterol is not a miracle supplement for athletes. While it may have some potential benefits, its adverse effects and potential for abuse far outweigh any potential gains. Furthermore, its use is prohibited by major sports organizations, making it a risky choice for athletes looking to improve their performance.
As an experienced researcher in the field of sports pharmacology, I would advise athletes to steer clear of clenbuterol and instead focus on proper nutrition and training to achieve their goals. There are no shortcuts to success, and the potential risks associated with clenbuterol are not worth the potential gains.
References
- Kier, A.B., et al. (2018). Chronic administration of clenbuterol induces cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in rats. Toxicology Letters, 295, 1-8.
- Knych, H.K., et al. (2014). Effects of clenbuterol administration on serum biochemical, histologic, and echocardiographic measurements of muscle injury in exercising horses. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 75(11), 997-1004.
- Van Eenoo, P., et al. (2010). Clenbuterol: a review of its use in food-producing animals. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, 27(7), 758-767.